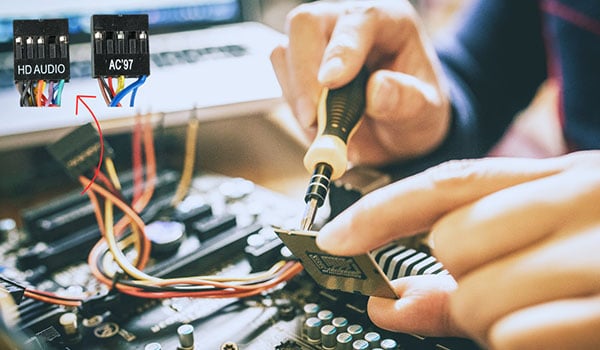
The AAFP header is usually located towards the bottom-left of a motherboard, though this can vary depending on the specific board layout. The primary purpose of the AAFP is to allow audio signals to be transmitted from the motherboard’s onboard audio solution to the front panel of the computer case. This allows users to plug in headphones, speakers, or microphones without reaching the computer’s back.
What is AAFP on Motherboard?
“AAFP” on a motherboard stands for “Analog Audio Front Panel.” It refers to a connector or header on the motherboard where the cables from the case’s front audio jacks (for headphones and microphones) are connected. This allows users to easily plug in audio devices like headphones or microphones directly at the front of their computer case rather than reaching to the back of the computer where the motherboard’s main audio jacks are located.
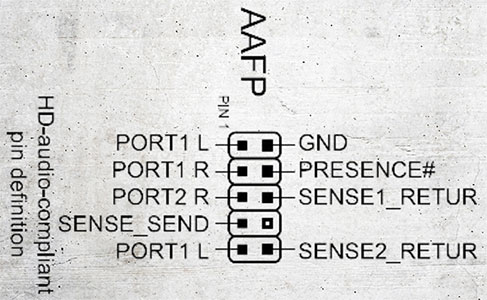
Here are some details regarding AAFP:
Pin Configuration: The AAFP connector on a motherboard is typically a 10-pin header, though one pin is missing to prevent reversed connections. This design ensures that the front panel audio cable can only be connected in the right orientation.
HD Audio vs. AC’97: Over the years, there have been two main standards for front-panel audio: HD Audio (sometimes referred to as Azalia) and the older AC’97. Most modern motherboards and cases support the HD Audio standard, but the AAFP connector accommodates either of the two standards based on how you connect the pins. Connecting the case’s front panel audio cable to the motherboard’s AAFP header following the correct standard is essential.
Features: Connecting to the AAFP allows for features like audio jack detection. For instance, when you plug headphones into the front panel jack, the motherboard can automatically mute the rear audio output, ensuring that sound is only directed to your headphones.
Location: The AAFP header is typically located towards the bottom-left corner of the motherboard, though this can vary based on the motherboard’s design.
Cable Management: When building a PC, route the front panel audio cable carefully. Because the AAFP header is far from the front panel, the cable needs to be long, making it crucial to manage it correctly to ensure clean cable management and proper airflow inside the case.
In summary, the AAFP on a motherboard provides an essential connection for front-panel audio functionalities, ensuring users have easy and convenient access to audio jacks. When building or upgrading a PC, always refer to the motherboard’s manual to correctly connect the front panel audio cable to the AAFP header.
AC’97 or HD Audio Connector?
AC’97 (Audio Codec’ 97) and HD Audio (High Definition Audio) are two audio standards for front panel audio connectors on computer cases. They represent different generations of audio standards, with AC’97 being older and HD Audio being the newer replacement.

Here’s a breakdown of the differences and features of each:
AC’97 (Audio Codec’ 97):
Age: AC’97 is an older audio standard prevalent in motherboards and computer cases produced in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Jack Sensing: AC’97 doesn’t support automatic jack sensing. If you plug headphones or a microphone into the front panel, the motherboard won’t automatically detect it.
Pin Assignment: The pin assignments for the AC’97 connector differ from those of HD Audio. If you connect an AC’97 front panel to an HD Audio header on a motherboard, it might not work correctly or could produce suboptimal audio quality.
HD Audio (High Definition Audio):
Age: In the mid-2000s, HD Audio replaced AC’97 as the new standard. Most modern motherboards and computer cases support HD Audio.
Jack Sensing: HD Audio supports automatic jack sensing. When you plug headphones into an HD Audio front panel, the motherboard can detect it and mute the rear audio output or make other adjustments accordingly.
Pin Assignment: The pin assignments for HD Audio are designed to be backward compatible with AC’97 to some extent, meaning that if you connect an HD Audio front panel to an AC’97 header on an older motherboard, it still works but with reduced functionality or quality.
Sound Quality: HD Audio generally offers better sound quality and supports more advanced features compared to AC’97.
Which to Use?
Check Compatibility: Before deciding which connector to use, check your motherboard’s specifications. Most modern motherboards will support HD Audio, but if you’re working with an older system, it may only support AC’97.
Go with HD Audio if Possible: Given a choice, it is the better option due to its superior sound quality, automatic jack sensing, and broader compatibility with modern systems.
Connection Caution: Be cautious about connecting an HD Audio front panel to an AC’97 motherboard header and vice versa. They are for some level of backward compatibility. There’s no guarantee of proper functionality or audio quality.
Refer to your motherboard’s manual for specific guidance on connecting front panel audio.
AAFP motherboard not working, how to fix it?
There are several reasons why the AAFP (Analog Audio Front Panel) on your motherboard isn’t working, meaning you’re not getting audio from the front panel headphone or microphone jacks. Here’s a step-by-step troubleshooting guide to help you diagnose and possibly fix the issue:
1. Check the Physical Connection
Ensure the front panel audio connector is securely plugged into the AAFP header on the motherboard. The pins should align correctly, and there shouldn’t be any loose connections.
Ensure that no pins are bent on the motherboard header.
2. Inspect the Cable
Check the cable running from the AAFP header to the front panel for any signs of damage.
If possible, test with another front panel audio connector to rule out issues with the cable.
3. Software & Driver Check
Make sure that the audio drivers for your motherboard are correctly installed. If unsure, visit the motherboard manufacturer’s website and download the latest audio drivers for your specific motherboard model.
Open the audio settings on your operating system to ensure that the correct playback device is set as default. Sometimes, the rear panel might be set as the default device, causing the front panel not to produce sound. Ensure that the audio is not muted and that the volume is set to an audible level.
4. BIOS/UEFI Settings
Some motherboards allow you to enable or disable the front panel audio from the BIOS/UEFI settings. Boot into your BIOS/UEFI and look for any audio settings to enable the front panel audio.
5. HD Audio vs. AC’97:
Some older cases have connectors for both HD Audio and AC’97. Ensure you’re using the correct one for your motherboard. Typically, modern motherboards support HD Audio, so that’s the one you should connect.
6. Test on Another System
If you have another compatible system available, try connecting your case’s front panel audio connector to that system. This can help determine if the problem is with the motherboard or the case.
7. Update BIOS
In rare cases, a BIOS update may resolve compatibility or functionality issues. Check the manufacturer’s website for any BIOS updates for your motherboard. Make sure to follow the BIOS update instructions carefully to avoid potential issues.
8. Reinstall Operating System
Reinstalling the OS can solve such problems. Ensure that you back up all essential data before proceeding.
9. Hardware Fault
If all the above steps don’t work, there may be a hardware fault, either with the motherboard’s AAFP header or the front panel audio jacks. You must RMA the motherboard or get a new case or a separate front-panel audio module in such cases.
Turn off and unplug your computer from the electrical outlet when working inside it to prevent potential electrical hazards. If you’re uncomfortable performing any of these steps, consider seeking help from a professional, or someone experienced in PC troubleshooting.
Learn more:
How To Flash Bios Without Display?
How To Clean Thermal Paste Off CPU?
Table of Contents